In November, the average sale price in the real estate market was $640,198, reflecting a 5.9% increase compared to the same month last year. This rise in prices highlights the ongoing demand and value in the market. Sales activity also saw a significant boost, with 614 transactions, marking a 35.5% increase year-over-year. New listings saw a significant rise of 10.8% year-to-date, providing more options for buyers.
Kathy Amess, Chair of LSTAR, commented on these trends, saying, “The recent interest rate cuts have played a significant role in boosting market activity. Lower borrowing costs have made homeownership more accessible, driving up sales and expanding inventory. It’s encouraging to see such positive momentum, and we remain committed to working with all stakeholders to ensure a vibrant and affordable housing market for everyone.” Future expectations for interest rates in Canada suggest a potential for further reductions. The Bank of Canada has already implemented several rate cuts in 2024, bringing the policy rate down to 3.75% by October. These cuts are aimed at supporting economic growth and controlling inflation.
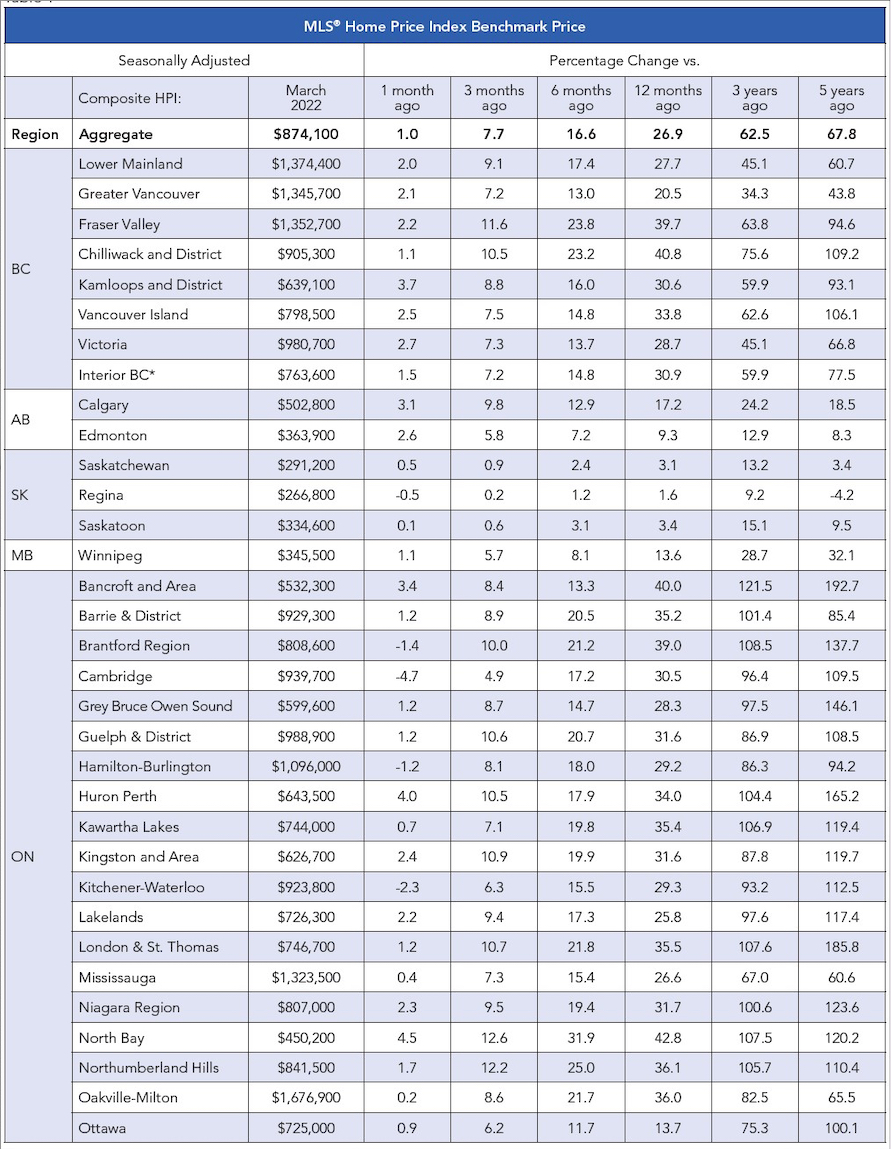
The table below displays November average prices and MLS® HPI Benchmark Prices in LSTAR’s main regions supplied by the Canadian Real Estate Association (CREA).
| Area
|
November 2024 MLS®
HPI Benchmark Price
|
November 2024
Average Price
|
| Central Elgin |
$641,900 |
$797,850 |
| London East |
$485,500 |
$515,978 |
| London North |
$714,300 |
$684,820 |
| London South |
$613,500 |
$639,990 |
| Middlesex Centre |
$878,000 |
$1,131,763 |
| St. Thomas |
$557,100 |
$565,269 |
| Strathroy-Caradoc |
$804,800 |
$639,863 |
| LSTAR |
$612,100 |
$640,198 |
The HPI benchmark price reflects the value of a “typical home” as assigned by buyers in a certain area based on various housing attributes, while the average sales price is calculated by adding all the sale prices for homes sold and dividing that total by the number of homes sold. The HPI benchmark price is helpful to gauge trends over time since averages may fluctuate by changes in the mix of sales activity from one month to the next.
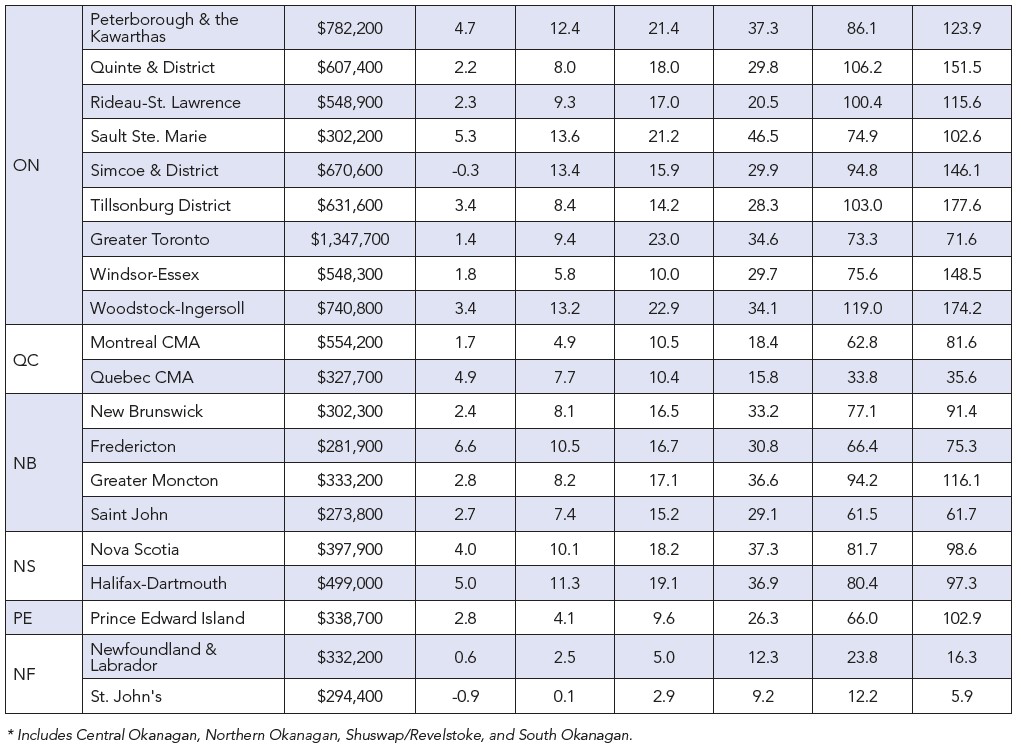
The following table displays November benchmark prices for all housing types within LSTAR’s jurisdiction and shows how they compare with those recorded in the previous month and three months ago.
| MLS® Home Price Index Benchmark Prices
|
| Benchmark Type |
November 2024 |
Change Over
October 2024 |
Change Over
August 2024 |
| LSTAR Composite |
$612,100 |
↑0.6% |
↓1.8% |
| LSTAR Single-Family |
$636,100 |
↑1.2% |
↓0.9% |
| LSTAR One Storey |
$595,400 |
↑1.9% |
↑0.2% |
| LSTAR Two Storey |
$718,300 |
↑0.8% |
↓1.3% |
| LSTAR Townhouse |
$492,200 |
↑1.0% |
↓3.5% |
| LSTAR Apartment |
$373,700 |
↓9.4% |
↓12.6% |
The real estate market in November showed several positive trends across different property types. The composite benchmark price reached $612,100, reflecting a steady 0.6% increase. Single-family homes saw a notable rise to $663,100, up by 1.2%, while one-storey homes increased by 1.9% to $595,400. Two-storey homes also experienced growth, with prices climbing by 0.8% to $718,300. Townhouses maintained stability with a 1.0% increase, reaching $492,200. Despite a slight decrease in apartment prices, the overall market remains strong, showcasing resilience and adaptability.
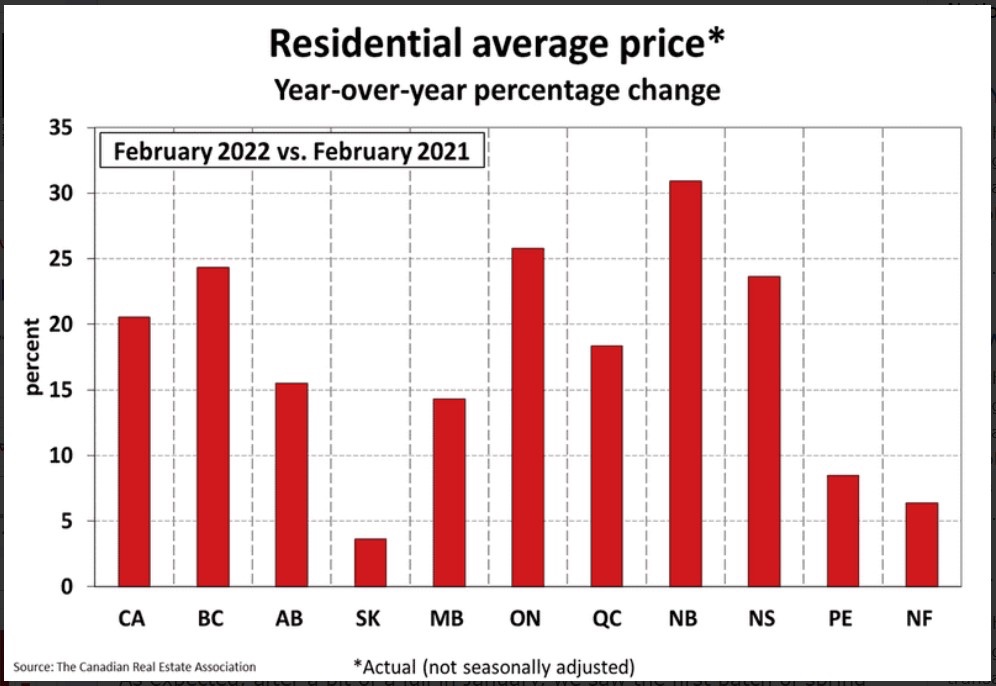
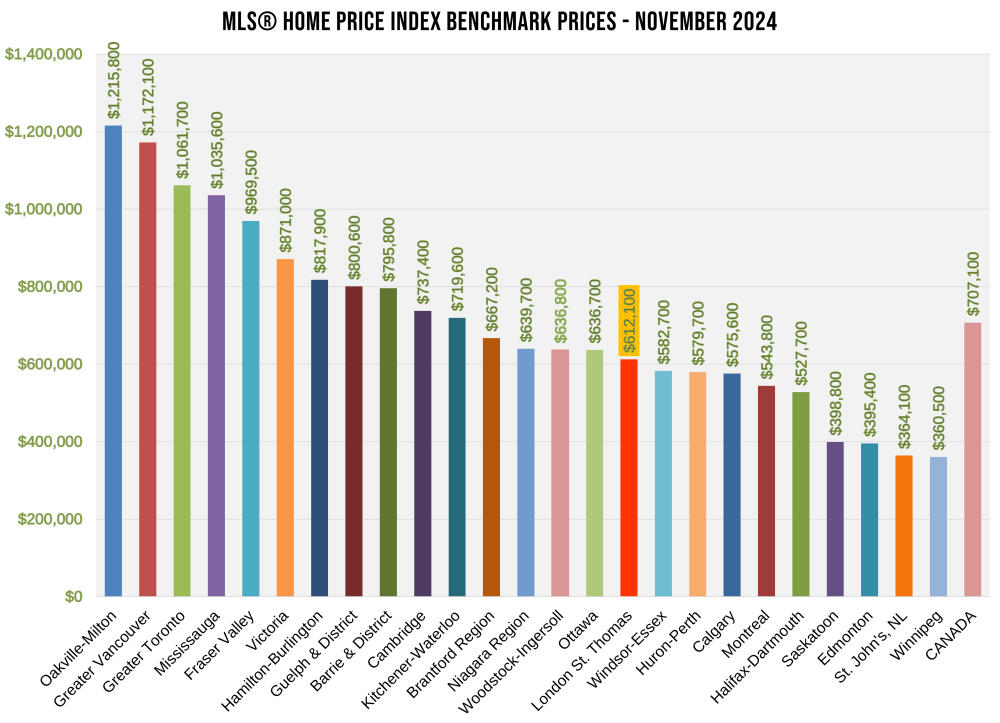
The chart below shows the most recent HPI benchmark prices across Canada.
“London and St. Thomas continue to offer exceptional value in the Canadian real estate market. With a benchmark price of $612,100, our region remains one of the most affordable among major centers. This affordability, combined with our vibrant community and quality of life, makes London and St. Thomas an attractive destination for homebuyers. Compared to cities like Oakville-Milton at $1,215,800 and Greater Vancouver at $1,117,100, our market provides a more accessible entry point for families and individuals looking to invest in their future,” said Amess.
Working with a local realtor is crucial in navigating this competitive market. Local realtors have in-depth knowledge of the area, including neighborhood trends and pricing strategies, which can help buyers and sellers make informed decisions and maximize their investment potential.
According to a recent study1 by Altus Group, an average housing transaction in Ontario generated an average of $88,966 in spin-off spending per transaction from 2020 to 2022. These expenses include legal fees, appraisers, moving costs, new appliances, and home renovation expenses.
“The home sales in November potentially generated more than $54 million, reinforcing the economic engine of the business of real estate,” Amess said.
Employment resulting from home sales is also significant, according to the Altus study. Resale housing activity created an estimated 106,565 jobs annually in Ontario from 2020 to 2022. Jobs include manufacturing, construction, finance, and insurance.
https://www.lstar.ca/story/interest-rate-cuts-fuel-november-real-estate-market-increase